Examples of essential questions to ask when structuring a digital marketing audit
Auditing your digital marketing activities is an essential technique to start a digital marketing strategy. But they’re also useful for finding opportunities to improve your digital marketing by identifying priorities you need to act on to get better results.
Knowing where to start and what to include can be difficult since although you may have your own area of expertise such as search, social media or business, you may not know about other topics. In this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive checklist you can use for your business based on the Smart Insights RACE Digital marketing framework. Each of the five parts of RACE is broken down into five to give a comprehensive evaluation of digital marketing for which I outline questions in this post.
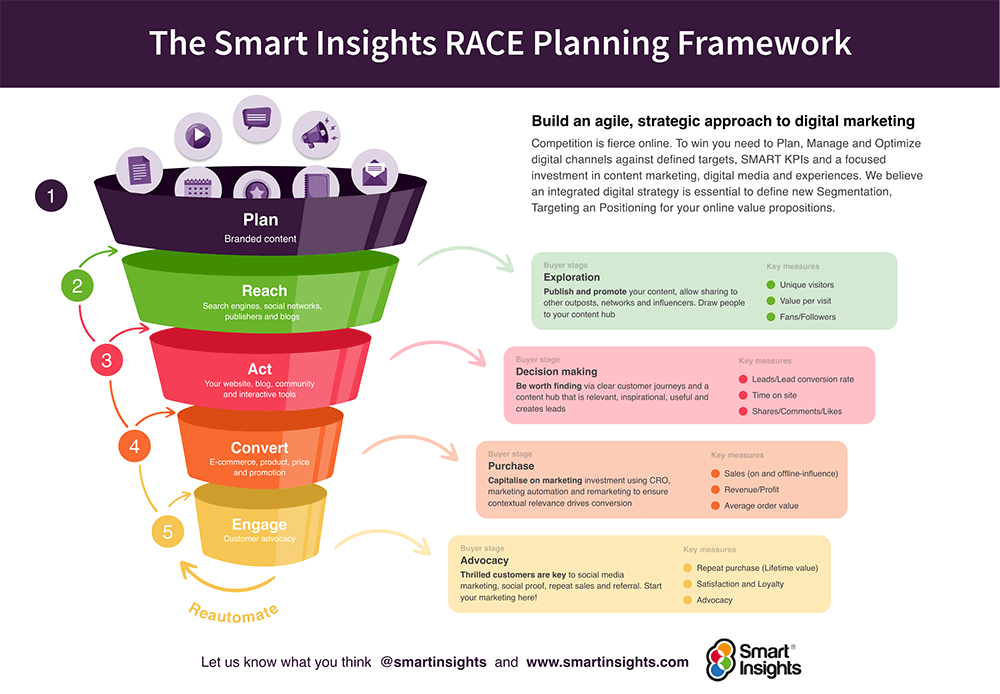
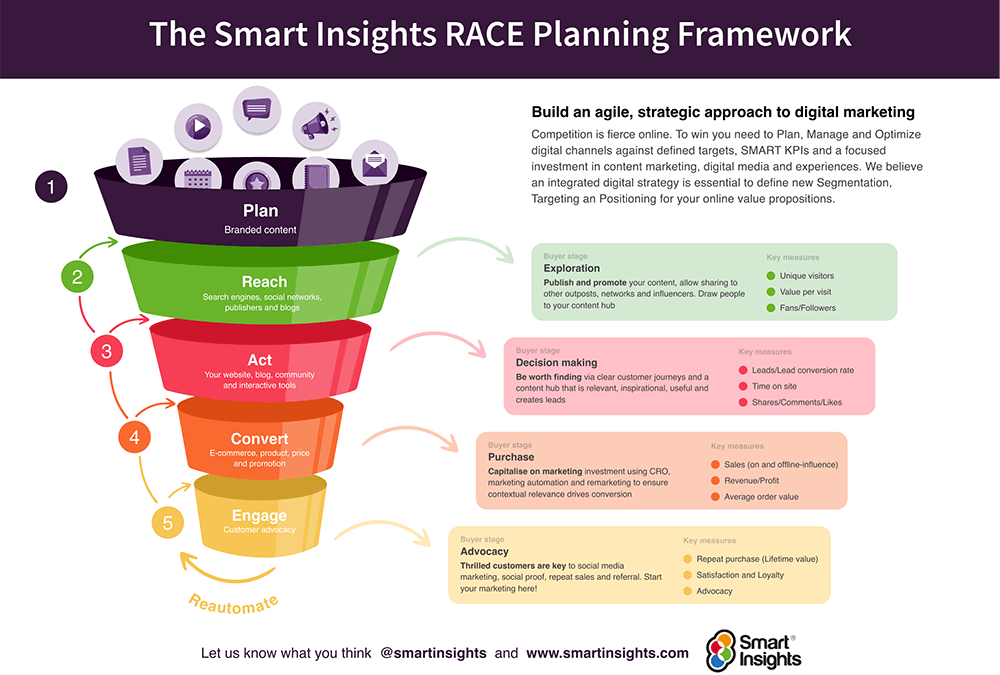
I developed this framework nearly 15 years ago based on my experience of consulting and training in digital marketing for businesses in a range of sectors and in companies of different sizes from small to large. Our auditing approach is a data-driven audit using tools to compare to your competitors and using your Google Analytics to assess the effectiveness of your marketing communications.
I’ve structured this audit based on the 5 key areas and within each, prompts for the questions you should be asking. To learn more about these concepts our members can the RACE Learning Path to drill into the details of how to complete the analysis with downloadable templates to assist. See our digital marketing audit template for a customisable spreadsheet you can amend for your business or your clients.
1. Plan – Auditing your resources and strategy process
How you manage digital marketing is often forgotten in a digital marketing audit that often focuses on channels, but it’s important to consider your overall process, strategy and resources, so you should start here, whether reviewing with a small business owner or the person responsible for digital marketing in a larger business. Issues to consider are:
- Performance – Do you have a dashboard to report performance? Can you break down performance by channel standardised using Analytics UTM tracking to track email marketing for example?
- Marketplace analysis – Who are your target customers? Have you defined personas? What is your success in reaching and converting them? Benchmarking visits and where possible conversions against competitors?
- Objectives – Do you set forecasts for generating visits leads and sales based on conversion funnel models (also available to members).
- Capabilities – these include your team – who is responsible for digital marketing – internal staff and agencies? What are their strengths and weaknesses? Are there any training gaps? This also includes marketing technology and tools which we cover in our essential marketing tools download.
- Strategies – Is there a strategy in place? How does your brand positioning compare to competitors? What is our defined target audience. Is there a 90-day planning or quarterly business review process?
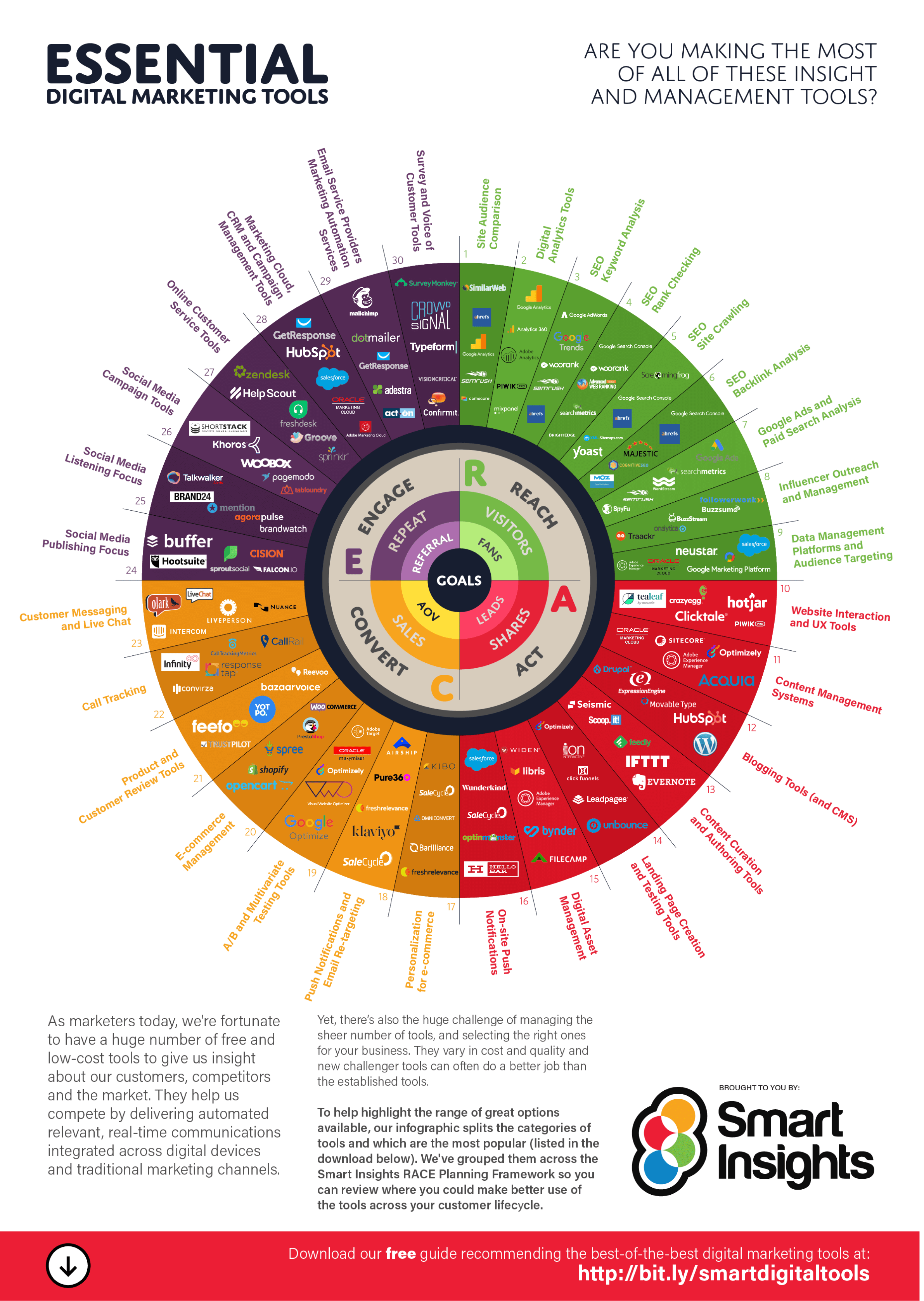
2. Reach – The Media audit
This review should compare your techniques for using Paid, Owned and Earned media (POEM) for acquiring traffic. Start by reviewing measurement of media and conclude by creating and digital acquisition plan with priorities.
- Media effectiveness – Use your Google Analytics to review the relative importance of different channels for VQVC – Volume, Quality, Value and Cost measures. What do attribution models suggest about the value of awareness-raising media such as display advertising and paid social?
- Organic search sources – What is the split of brand vs non-brand search terms? Are International, Local and Mobile vs Desktop as expected?
- Organic search checklist – Domain authority based on backlink profile of unique-linking domains. Use of on-page ranking factors. Our SEO Learning Path explains the details on these and references our organic search audit template
- Paid search – What is the split of brand vs non-brand ad traffic for different sources, what is the Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS) for each? How does the quality score vary across campaigns?
- Earned media – How are we using digital PR and influencer marketing? Is it a structured or ad hoc approach?
- Social media – How does traffic volume and quality compare for paid and organic social for each of the main social platforms you use?
3. Act – Auditing website customer journeys and content for lead generation
After reviewing the success of your media channels in driving traffic, the logical next step is to audit the effectiveness of the customer journeys on the site in supporting content engagement and lead generation. This is the main aim of the Act stage. Key factors to assess are:
- Customer journeys – What are the main customer journeys based on landing pages and top content? Our visual suggests the complexity of the analysis and testing we need to improve journeys and conversion since there are so many different entry points into the site and different types of pages and panels within pages need to persuade audiences.
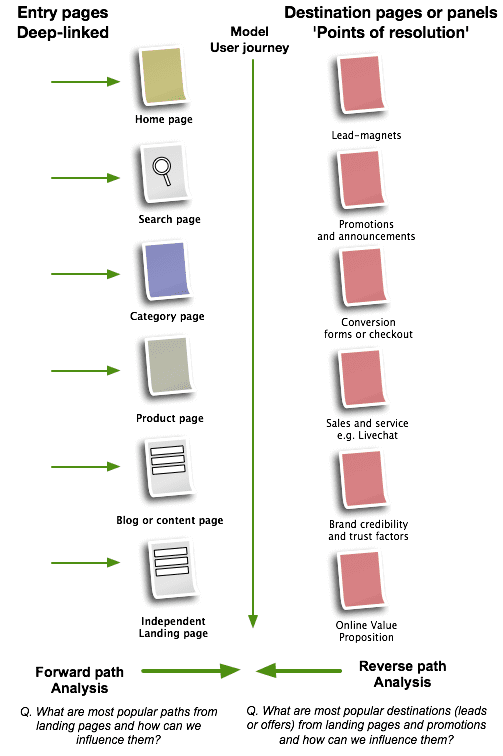
Our visual suggests the complexity of the analysis and testing we need to make happen to improve journeys and conversion since there are so many different entry points into the site and different types of pages and panels within pages need to persuade audiences.
- Content marketing strategy. Is there a defined content marketing strategy to serve relevant content throughout the customer journey to meet your objectives?
This is a vital activity since Content Marketing is at the heart of digital marketing and impacts not only customer journeys and conversion and is based on audience needs, but also media techniques for content distribution like organic search, paid search, social media and email marketing automation.
A content marketing strategy defines:
- Your goals for CM
- Your audience personas
- Content selection mapped against customer journeys and lifecycle
- Editorial calendar for content publication
- Content distribution plan including POE media and influencer outreach
- Tracking to achieve ROI
- Landing Page effectiveness – First impressions are important, we don’t want our visitors to leave immediately, so the audit should review whether landing pages optimized in line with best practices using a structured improvement approach?
- Lead capture and audience profiling – Are we following best practices for lead capture and profiling, scoring and working to improve them in a structured way? This is covered in our e-learning topic on this activity.
- Campaign and Content Planning – Do we have a clear campaign planning and improvement approach so that digital campaigns are integrated with marketing campaigns. Access our toolkit which has templates to help you plan and manage campaigns better to improve results: Marketing Campaign planning
4. Convert – Auditing conversion efficiency
Success factors to review within the RACE framework for conversion are based on these questions:
- Retargeting. Are you using on and off-site retargeting to convert your audience to sale?
It’s a common situation that a visitor will only interact with a website or brand once, even after subscribing. This makes retargeting or reminders which are powerful and cost-effective technique to encourage people to return and ultimately buy.
- Web Personalization. Are personalized containers used on the site with recommended product, content or offers?
On-site personalisation is also a technique that is commonly used on retail and e-commerce sites, but under-utilised on other sites. The options and some of the technologies are covered in our e-learning.
- Mobile experience. Are the techniques used for interaction and conversion effective on mobile?
This question applies across all the previous ACT and CONVERT sections, but are referencedhere since conversion is a specific problem on mobile.
- Multichannel selling. Are offline interactions prompted to encourage visitors to convert?
Direct interactions with real people, your employees, almost always have higher conversion rates than unassisted on-page website conversion. This is why options like Livechat have increased in popularity.
- Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO). Is there a programme of structured testing and improvement for conversion?
Using a test-learn-refine approach across the best practice techniques discussed above WILL produce uplift if the programme is sustained since not every AB test will produce a positive result.
5. Engage – Customer Engagement
‘Engage’ is aimed at achieving long-term customer engagement. In digital marketing, there is a tendency to focus too much on the short-term engagement, but it’s the long-term engagement that matters to results.
You can see from the RACE visual that key measures are around increasing repeat purchases and developing customer satisfaction, loyalty and advocacy.
- Customer Onboarding and growth. What is the quality of the online customer onboarding?
These are similar to the welcome sequence for retargeting, but within a different goal – to develop brand preference, gain feedback, e.g. through reviews and ratings and encourage repeat purchase.
- Customer Digital Experiences. What are the processes and tools you use to review and improve the customer experience?
These are activities that tend to be better setup in larger organisations, but they are equally important in smaller businesses!
- Customer Service and Success. How are customer service processes and quality of support content assessed?
How can people, process, tools and measurement be used to improve quality of experience?
- Customer Email marketing. How is the quality of email marketing improved across the customer lifecycle?
This is a major activity which is impacted by many of the other activities in this audit.
We have a separate Email marketing audit we recommend you review as part of this activity.
Given the importance of email marketing, we have a separate toolkit covering how to create an email marketing strategy and practical templates to improve your email marketing:
- Improve social media marketing. How is the quality of social media marketing improved across the customer lifecycle?
Like email marketing. This is a major activity which is impacted by many of the other activities in this audit.
We have separate Social media audits we recommend you review as part of this.
Given the importance of social media marketing across each part of RACE, we have a separate toolkit covering how to create a social media strategy and practical ‘Smarter’ guides for each of the main social media platforms.
Summary
When completing the digital marketing audit, make sure that you cover both strategy, customer acquisition and retention. The most important aspects to consider are Reach and Act since success in these is essential to power your digital marketing.